Definition, Applications, and Illustrations of Contracts for Differences (CFDs)
Understanding Contract for Differences (CFD) Contract for Differences (CFD) is a financial derivative that settles the price differences between opening and closing trades through cash payments. Unlike traditional trading, CFDs…
Understanding the E-Mini and Its Applications in Futures Trading
What Are E-minis? E-minis are electronically traded futures contracts that represent a smaller fraction of the value of standard contracts and are popular for trading indexes, commodities, and currencies. Introduced…
Understanding the Role of a Floor Trader: Definition, Responsibilities, and Qualifications
What Is a Floor Trader? A floor trader is a vital exchange member who executes transactions exclusively for their own account from the floor of the exchange. Traditionally, floor traders…
Definition, Role, and Registration of Futures Commission Merchant (FCM)
What is a Futures Commission Merchant – FCM A pivotal player in the world of futures trading, a Futures Commission Merchant (FCM) serves as the bridge connecting customers to the…
Understanding Futures Contracts: Varieties, Operations, and Applications in the Trading World
Understanding Futures Contracts A futures contract is a legally binding agreement to exchange a specific commodity, asset, or security at a predetermined price on a specified future date. These contracts…
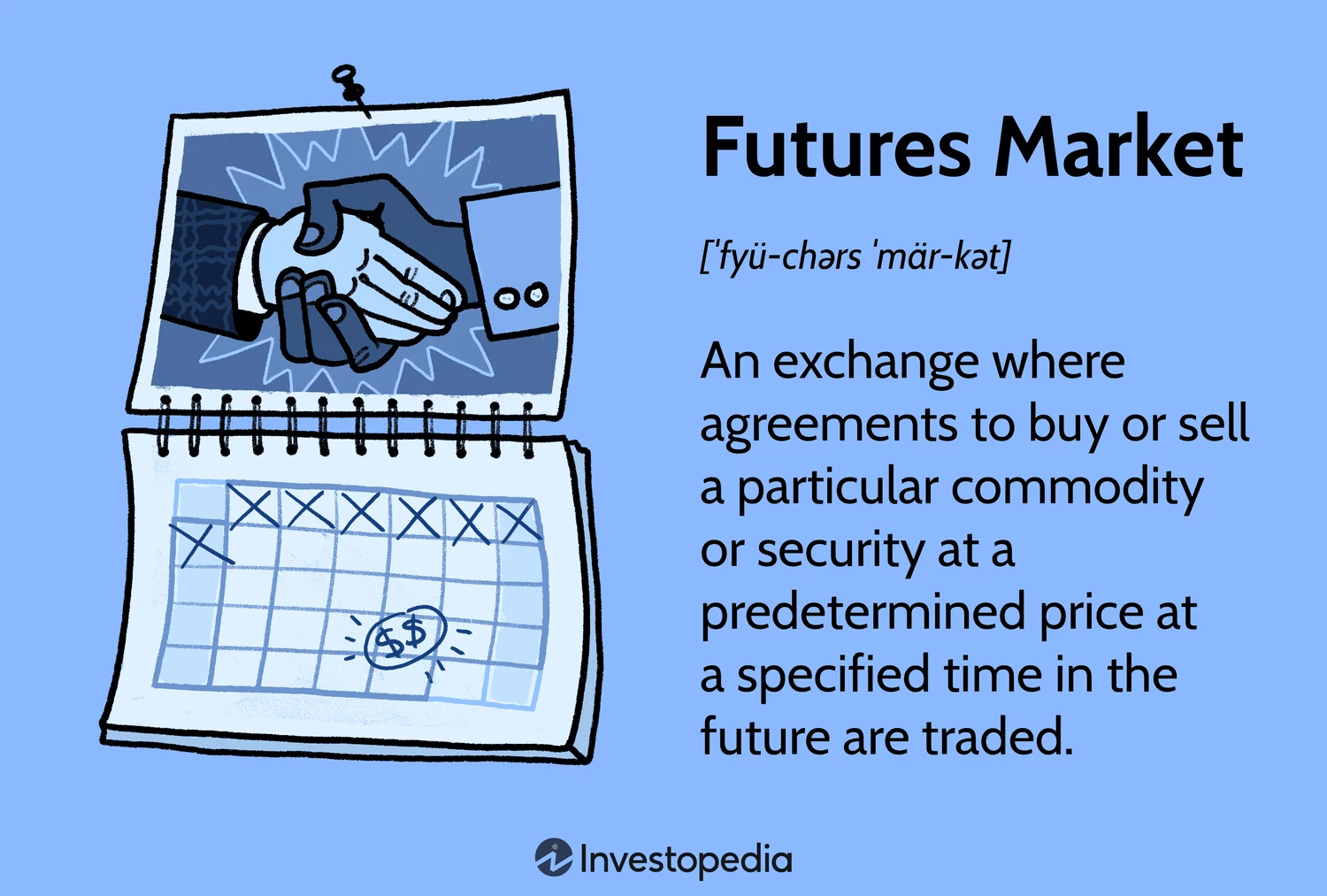
Market for futures trading
What Is a Futures Market? A futures market serves as an auction platform where traders engage in the buying and selling of commodity and futures contracts for future delivery. These…
Understanding Bond Futures: Definition, Operation, and Purchasing Process
Bond futures are financial instruments that involve the purchase or sale of a bond on a specified future date at a predetermined price. These contracts trade on futures exchanges and…
Purchasing on Margin: Process, Dangers, and Benefits
Understanding Buying on Margin Buying on margin involves investors purchasing assets by borrowing funds from banks or brokers. It entails an initial payment to the broker, such as a 10%…
Definition and Example of Cash-and-Carry Arbitrage
What is Cash-and-Carry-Arbitrage Cash-and-carry-arbitrage is a strategic approach that involves simultaneously buying an asset in the cash market and selling (shorting) a futures contract on the same underlying asset. This…
Definition and Calculation Formula of Cheapest to Deliver (CTD)
What Is Cheapest to Deliver? In the realm of futures contracts, the term “cheapest to deliver” (CTD) denotes the most cost-effective security that can be delivered to fulfill the obligations…